Read Tuple and Array Through Text File
Tuple is a collection of Python objects much like a list. The sequence of values stored in a tuple can be of any type, and they are indexed by integers.
Values of a tuple are syntactically separated by 'commas'. Although it is not necessary, it is more common to ascertain a tuple by closing the sequence of values in parentheses. This helps in agreement the Python tuples more than easily.
Creating a Tuple
In Python, tuples are created by placing a sequence of values separated by 'comma' with or without the use of parentheses for grouping the data sequence.
Note: Creation of Python tuple without the use of parentheses is known as Tuple Packing.
Python program to demonstrate the addition of elements in a Tuple.
Python3
Tuple1 = ()
impress ( "Initial empty Tuple: " )
print (Tuple1)
Tuple1 = ( 'Geeks' , 'For' )
print ( "\nTuple with the use of String: " )
print (Tuple1)
list1 = [ one , 2 , iv , 5 , 6 ]
print ( "\nTuple using Listing: " )
print ( tuple (list1))
Tuple1 = tuple ( 'Geeks' )
impress ( "\nTuple with the use of function: " )
impress (Tuple1)
Output:
Initial empty Tuple: () Tuple with the use of Cord: ('Geeks', 'For') Tuple using Listing: (1, 2, four, 5, 6) Tuple with the use of office: ('Chiliad', 'due east', 'east', 'one thousand', 's') Creating a Tuple with Mixed Datatypes.
Tuples can incorporate whatsoever number of elements and of whatsoever datatype (similar strings, integers, list, etc.). Tuples can also be created with a single element, merely it is a bit tricky. Having one element in the parentheses is not sufficient, at that place must be a trailing 'comma' to make information technology a tuple.
Python3
Tuple1 = ( 5 , 'Welcome' , 7 , 'Geeks' )
print ( "\nTuple with Mixed Datatypes: " )
print (Tuple1)
Tuple1 = ( 0 , i , ii , three )
Tuple2 = ( 'python' , 'geek' )
Tuple3 = (Tuple1, Tuple2)
print ( "\nTuple with nested tuples: " )
print (Tuple3)
Tuple1 = ( 'Geeks' ,) * iii
impress ( "\nTuple with repetition: " )
impress (Tuple1)
Tuple1 = ( 'Geeks' )
northward = five
print ( "\nTuple with a loop" )
for i in range ( int (n)):
Tuple1 = (Tuple1,)
print (Tuple1)
Output:
Tuple with Mixed Datatypes: (5, 'Welcome', vii, 'Geeks') Tuple with nested tuples: ((0, ane, two, 3), ('python', 'geek')) Tuple with repetition: ('Geeks', 'Geeks', 'Geeks') Tuple with a loop ('Geeks',) (('Geeks',),) ((('Geeks',),),) (((('Geeks',),),),) ((((('Geeks',),),),),) Accessing of Tuples
Tuples are immutable, and normally, they comprise a sequence of heterogeneous elements that are accessed via unpacking or indexing (or fifty-fifty by attribute in the case of named tuples). Lists are mutable, and their elements are usually homogeneous and are accessed by iterating over the list.
Note: In unpacking of tuple number of variables on the left-hand side should be equal to a number of values in given tuple a.
Python3
Tuple1 = tuple ( "Geeks" )
impress ( "\nFirst element of Tuple: " )
print (Tuple1[ 0 ])
Tuple1 = ( "Geeks" , "For" , "Geeks" )
a, b, c = Tuple1
impress ( "\nValues after unpacking: " )
impress (a)
print (b)
print (c)
Output:
First element of Tuple: G Values after unpacking: Geeks For Geeks
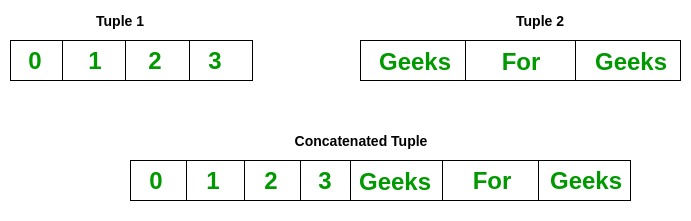
Concatenation of Tuples
Concatenation of tuple is the process of joining two or more than Tuples. Concatenation is washed by the use of '+' operator. Concatenation of tuples is washed always from the end of the original tuple. Other arithmetic operations do not apply on Tuples.
Annotation- Only the aforementioned datatypes can be combined with concatenation, an fault arises if a list and a tuple are combined.
Python3
Tuple1 = ( 0 , 1 , two , 3 )
Tuple2 = ( 'Geeks' , 'For' , 'Geeks' )
Tuple3 = Tuple1 + Tuple2
print ( "Tuple 1: " )
print (Tuple1)
print ( "\nTuple2: " )
print (Tuple2)
print ( "\nTuples after Concatenation: " )
print (Tuple3)
Output:
Tuple ane: (0, 1, 2, 3) Tuple2: ('Geeks', 'For', 'Geeks') Tuples after Concatenation: (0, 1, 2, 3, 'Geeks', 'For', 'Geeks') Slicing of Tuple
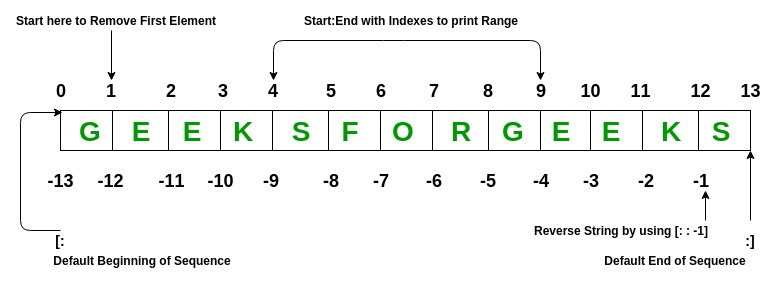
Slicing of a Tuple is done to fetch a specific range or slice of sub-elements from a Tuple. Slicing tin also be done to lists and arrays. Indexing in a list results to fetching a unmarried element whereas Slicing allows to fetch a set of elements.
Notation- Negative Increment values can also be used to reverse the sequence of Tuples.
Python3
Tuple1 = tuple ( 'GEEKSFORGEEKS' )
print ( "Removal of First Element: " )
print (Tuple1[ i :])
impress ( "\nTuple after sequence of Element is reversed: " )
print (Tuple1[:: - 1 ])
print ( "\nPrinting elements between Range iv-nine: " )
print (Tuple1[ iv : 9 ])
Output:
Removal of First Element: ('E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F', 'O', 'R', 'Grand', 'Due east', 'East', 'Chiliad', 'S') Tuple after sequence of Element is reversed: ('S', 'K', 'E', 'E', 'Thou', 'R', 'O', 'F', 'S', 'Yard', 'E', 'E', 'Thousand') Printing elements between Range 4-9: ('S', 'F', 'O', 'R', 'Grand') Deleting a Tuple
Tuples are immutable and hence they do not allow deletion of a function of it. The entire tuple gets deleted by the use of del() method.
Note- Press of Tuple after deletion results in an Fault.
Python
Tuple1 = ( 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , four )
del Tuple1
impress (Tuple1)
Traceback (most contempo phone call concluding):
File "/home/efa50fd0709dec08434191f32275928a.py", line 7, in
impress(Tuple1)
NameError: name 'Tuple1' is not defined
Built-In Methods
| Built-in-Method | Description |
|---|---|
| alphabetize( ) | Observe in the tuple and returns the index of the given value where it'south available |
| count( ) | Returns the frequency of occurrence of a specified value |
Built-In Functions
| Born Office | Clarification |
|---|---|
| all() | Returns truthful if all element are true or if tuple is empty |
| any() | return truthful if any element of the tuple is true. if tuple is empty, return simulated |
| len() | Returns length of the tuple or size of the tuple |
| enumerate() | Returns enumerate object of tuple |
| max() | return maximum chemical element of given tuple |
| min() | return minimum element of given tuple |
| sum() | Sums upward the numbers in the tuple |
| sorted() | input elements in the tuple and return a new sorted listing |
| tuple() | Convert an iterable to a tuple. |
Contempo Articles on Tuple
Tuples Programs
- Impress unique rows in a given boolean Strings
- Plan to generate all possible valid IP addresses from given string
- Python Dictionary to find mirror characters in a string
- Generate ii output strings depending upon occurrence of character in input string in Python
- Python groupby method to remove all consecutive duplicates
- Convert a list of characters into a cord
- Remove empty tuples from a list
- Reversing a Tuple
- Python Set symmetric_difference()
- Convert a listing of Tuples into Dictionary
- Sort a tuple by its float element
- Count occurrences of an element in a Tuple
- Count the elements in a list until an element is a Tuple
- Sort Tuples in Increasing Order by any key
- Namedtuple in Python
Useful Links:
- Output of Python Programs
- Recent Articles on Python Tuples
- Multiple Choice Questions – Python
- All articles in Python Category
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-tuples/
0 Response to "Read Tuple and Array Through Text File"
Post a Comment